The case against negative rates for the US
By Steven Knight, Research Analyst, Blackwell Global The past few weeks have seen mounting speculation doing the rounds that the US Federal Reserve could potentially be contingency planning for the introduction of a negative interest rate policy (NIRP). Given the historically low Federal Funds Rate, and the lack of available monetary policy tools, NIRP might […]

By Steven Knight, Research Analyst, Blackwell Global
The past few weeks have seen mounting speculation doing the rounds that the US Federal Reserve could potentially be contingency planning for the introduction of a negative interest rate policy (NIRP). Given the historically low Federal Funds Rate, and the lack of available monetary policy tools, NIRP might seem the obvious choice in responding to a recession. However, there are some serious questions regarding the effectiveness of introducing a “tax” on banking.
Obviously, negative interest rates have been at the forefront of debate over the past month given their introduction in Japan, as well as some concerning rhetoric from the US Fed regarding the “legality” of their use within the economy. In fact, given the expectation setting by both the Fed’s Kocherlakota and Kashkari, it is highly likely that NIRP currently forms part of the central banks response if a recession was to become apparent. Subsequently, a robust discussion of breaching the zero lower bound as a stimulative tool is highly appropriate.
Firstly, it is important to note that negative interest rates are a relatively new tool in the monetary policy tool bag for central banks. Although the Swedish Central Bank was the first to introduce them in 2009, their ultimate effectiveness is arguable. The introduction of negative rates, albeit at a wholesale level, is largely seen as a tax on the holding of money. The intent was to dis-incentivise the hoarding of capital by financial institutions and to stimulate lending and credit growth.
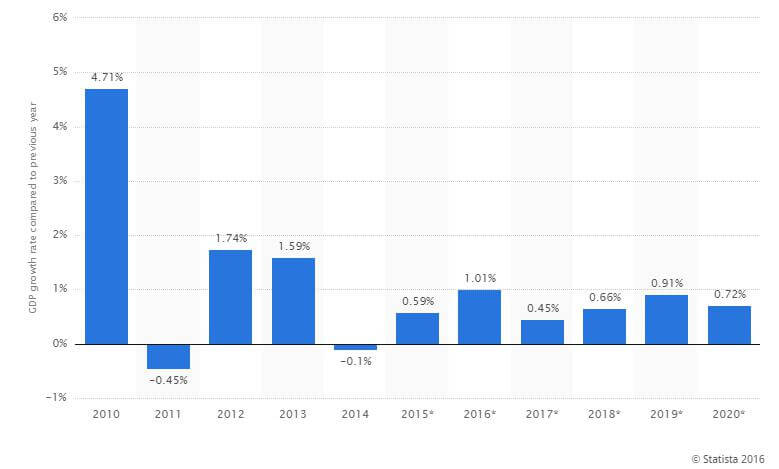
However, the jury is largely still out on the overall effectiveness of the NIRP policy, especially when you consider the sagging GDP growth in both the Eurozone and Japan, both of whom have undertaken negative rate campaigns. Subsequently, there is likely to be a bevy of PhD dissertations in the next ten years targeting both NIRP and QE.
One of the inherent risks of NIRP policies is the passing of these costs through the pass-through channels to consumers. Although this doesn’t appear to have directly occurred, as far as retail rates, it is highly likely that banks have found ways to defray the expense through additional fees on accounts and services. Subsequently, there is a long-term concern as to whether this incentivises the move back towards physical currency and would lead to consumer withdrawals rather than simply an increase in spending, consumption, and investment.
In addition, in a globalised world, capital typically flows to where yields are present and NIRP policies actually incentivise capital outflows to other markets.
Point in case, prior to the recent Fed rate hike, global currency markets were beset by capital seeking the widening interest rate differentials in other currencies such as the NZD and AUD (known as a carry trade). Subsequently, these markets were somewhat distorted as injected capital effectively found its way offshore to where the yields were present, thereby artificially increasing exchange rates and demand for those pairs. This has clearly also had an impact on the export trade demand for many economies, especially given the large swings within valuations.
Additionally, NIRP imposes some additional reporting and forecasting problems for Central Banks. Much of the current framework for predicting and forecasting the economy largely relies upon econometric models that assume a relationship between money, interest rates, savings, and investment. Unfortunately, when you upset the apple cart with negative rates, it changes many of these relationships and the econometric forecasting models start to break down.
In fact, NIRP and QE may explain why we have seen a move away from the use of the Taylor rule and Phillips Curve amongst some central banks. This ultimately leads to a risk of increased timing errors by the very institutions that were meant to be stimulating growth a price stability.
Although, many would consider that consumers purchasing power has already largely been eroded by inflation over the past few years NIRP could be the ultimate double whammy as they lose their purchasing power in real terms, along with having a form of increased fees/costs to hold money foist upon them. This could lead to some significant changes in how consumers perceive digital and physical currency, which is a slippery slope indeed.
Ultimately, I suspect that central banks will learn that there is a limit to the effectiveness of their monetary policy and management of the economy. It begs the question, at what point should fiscal policy step up and be used to buoy an economy and smooth out the business cycle. I suspect that the answer to that question is that the economy should look towards Fiscal policy when rates reach the zero-lower-bound, lest large distortions in financial markets and the velocity of money are to occur.